Image Credit: Press Information Bureau
4 Indian Scientists Win Praise For Their Breakthrough In Converting CO2 To Methane
Writer: Ratika Rana
Her primary objective is to inform, promote, educate and cultivate readers through writing.
Karnataka, 22 Nov 2021 11:16 AM GMT
Editor : Ankita Singh |
A literature lover who likes delving deeper into a wide range of societal issues and expresses her opinions about the same. Keeps looking for best-read recommendations while enjoying her coffee and tea.
Creatives : Ratika Rana
Her primary objective is to inform, promote, educate and cultivate readers through writing.
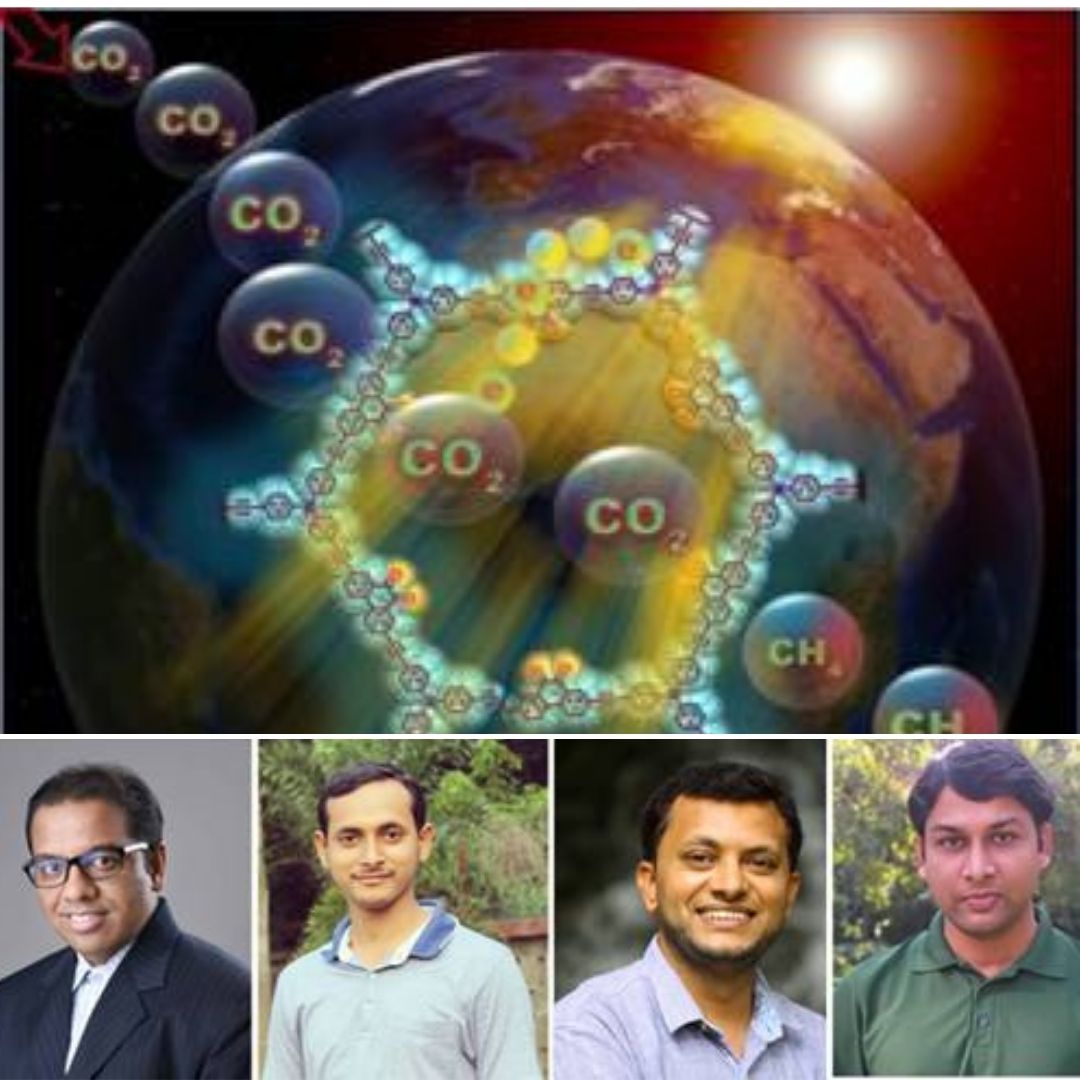
Ongoing research by four scientists is making a significant effort to reduce carbon dioxide into value-added products, methane (CH4) could be one of the value-added products with significant uses as the cleanest burning fossil fuel.
Four scientists from Bengaluru's Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research have designed a cost-effective metal-free catalyst to convert carbon dioxide into methane to absorb visible light. Methane could also be one of the value-added products of carbon, with considerable uses, making it the cleanest burning fossil fuel. Scientists have developed the metal-free porous organic polymer in such a manner that it would absorb visible light and further, catalyze the carbon dioxide reduction as well.
What Are The Key Requirements Of A Photo-Catalyst?
Some of the key requirements of a photo-catalyst, to convert carbon dioxide into value-added products are light-harvesting property, charge carrier (electron-hole pair) separation proficiency, and presence of proper electronically aligned conduction band. Therefore, it has always been a challenge to reduce CO2 to CH4 selectively and efficiently. Only a handful of catalysts are able to reduce CH4 selectively and efficiently, and most of the catalyst contains metal counterparts that are toxic and expensive, the Press Information Bureau reported.
The team of scientists consists of professor Tapas K Maji, Dr Soumitra Barman, Dr Ashish Singh and Faruk Ahamed Rahimi, and their work has been selected for publication in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, informed the Science ministry's official release. In the research project, the scientists have aimed to hit two targets with one arrow, one is producing value-added products that would reduce the carbon stress on the environment, and the second, to provide alternative fossil fuels.
What Is The Objective?
The four scientists aim to convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into methane through a photochemical process that utilizes solar energy as a renewable energy source. Currently, the four methods of carbon dioxide reduction are photochemical, electrochemical, photochemical and photothermal. Scientists have reportedly produced a robust and thermally stable conjugated microporous organic polymer using carbon and carbon coupling. The Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research is an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology under the Government of India.
Also Read: 17-Year-Old Tribal Girl From Kerala Qualifies For Beauty Pageant
 All section
All section