Credits: Wikimedia
'Welfare Schemes For Religious Minorites Legally Valid, Aims To Bridge Inequality': Centre Tells SC
Writer: Devyani Madaik
A media enthusiast, Devyani believes in learning on the job and there is nothing off limits when it comes to work. Writing is her passion and she is always ready for a debate as well.
India, 15 July 2021 7:35 AM GMT
Editor : Palak Agrawal |
Palak a journalism graduate believes in simplifying the complicated and writing about the extraordinary lives of ordinary people. She calls herself a " hodophile" or in layman words- a person who loves to travel.
Creatives : Devyani Madaik
A media enthusiast, Devyani believes in learning on the job and there is nothing off limits when it comes to work. Writing is her passion and she is always ready for a debate as well.
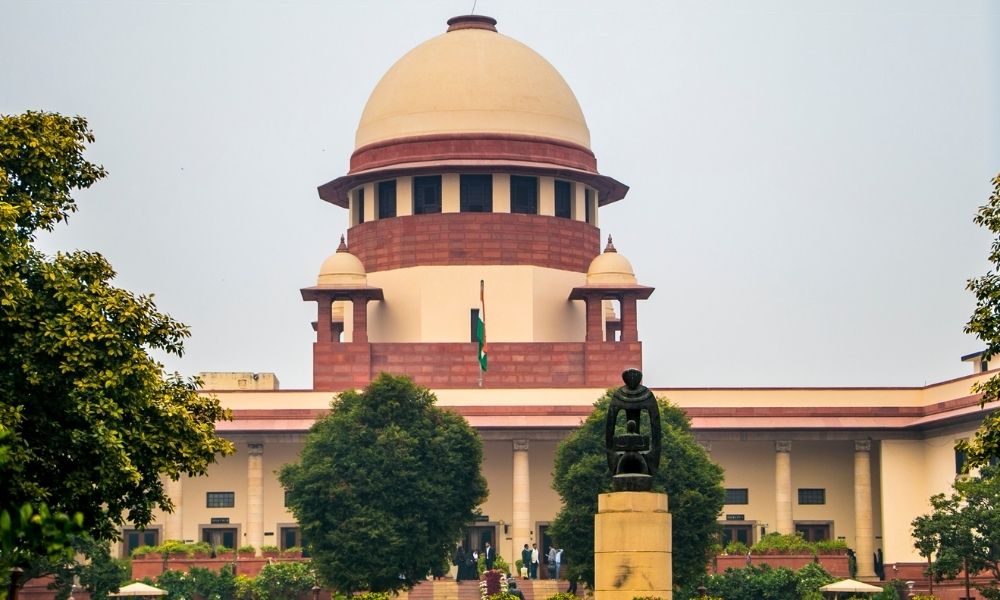
The government’s response was to a petition which said welfare schemes could not be based on religion. The petition also sought the scrapping of the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992, stating that there was already a Backward Classes Commission to list individuals who needed aid.
The welfare schemes for the religious minority communities of India are legally valid and do not violate the rights of the Hindus or other communities, the central government informed the Supreme Court.
The government's response was to a petition which said welfare schemes could not be based on religion.
Scrap National Commission for Minorities
The petition also sought the scrapping of the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992, stating that there was already a Backward Classes Commission to list individuals belonging to the economically weaker sections which need support.
The petitioners, Neeraj Shankar Saxena, and five others stated that they were unconstitutionally deprived of the benefits available to similar individuals of religious minorities, which violates their fundamental right, NDTV reported.
The petitioners said that the Muslim community members were receiving unfair advantages. The Centre was considering the community above the rule of law and Constitution, as the Hindu community availed no such benefits, they added.
"The petitioners and other Hindu community members are suffering because they have been born in the majority community. The State cannot promote or give any benefit to any religious community whether minority or majority is keeping in view the secular ethos embedded in the Constitution of India," the petition said, reported NDTV.
Better Opportunities Result Of Schemes
In its affidavit, the Centre said the schemes implemented aim to bridge the gap of inequality because of individuals belonging to a different caste and to improve the quality and level of education. In addition, employment opportunities, skills, and entrepreneurship development arise because of such schemes.
Several underprivileged children got an opportunity to turn their life around due to the welfare schemes.
The government said the schemes did not contradict the principles of equality embodied in the Constitution. "These schemes are legally valid as they are only enabling provisions to achieve inclusiveness and do not suffer from any infirmity. The support given to disadvantaged/ underprivileged children/ candidates of minorities communities through these schemes cannot, therefore, be faulted with," the affidavit further read.
Schemes For Disadvantaged
The Centre clarified that the schemes are meant for the individuals from economically weaker sections of the society and not for everyone belonging to a minority community. Quoting an example, the government mentioned the educational schemes, including coaching and scholarships, that have benefitted several students and are entirely based on academic merit.
Also Read: Gujarat Horror: Tribal Woman Paraded Naked, Forced To Carry Husband On Shoulders
 All section
All section