'Aditya-L1': ISRO Set To Launch India's First Dedicated Mission To Study Sun, All You Need To Know
Writer: Deepthi Rao
She is a postgraduate student pursuing Multimedia Journalism at Christ Deemed to be University. She believes in the power of storytelling and truth. "Do it with passion or not at all."
India, 29 Dec 2022 6:38 AM GMT
Editor : Shiva Chaudhary |
A post-graduate in Journalism and Mass Communication with relevant skills, specialising in content editing & writing. I believe in the precise dissemination of information based on facts to the public.
Creatives : Shiva Chaudhary
A post-graduate in Journalism and Mass Communication with relevant skills, specialising in content editing & writing. I believe in the precise dissemination of information based on facts to the public.
The enhanced Aditya-L1 project would provide a thorough knowledge of the Sun's dynamic processes and answer some significant problems in solar physics. It is scheduled to launch from Sriharikota in the first few months of 2023.
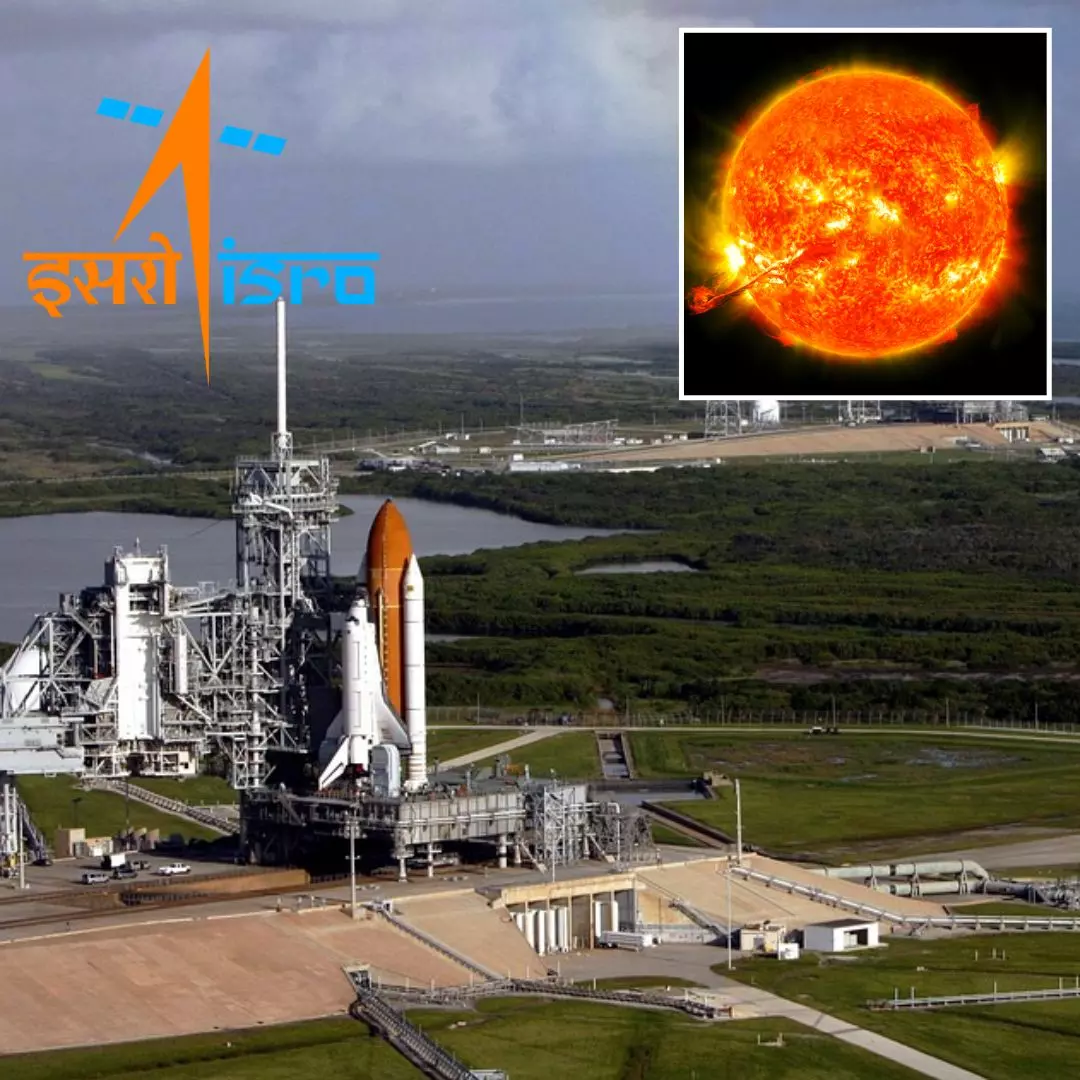
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is setting the stage to deploy Aditya-L1, the first dedicated mission of the country to study the Sun, into space in the first few months of 2023. Sankarasubramanian K was named the Principal Scientist of the Aditya-L1 mission in October 2022.
Following the successful launch of AstroSat in 2015, Aditya-L1 will be the second space-based project in India.
All Eyes On The Sun
Named after one of many Sanskrit names for the Sun- Aditya- is a planned mission of ISRO to study the star present at the centre of the Solar System. The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-XL) is scheduled to launch the Aditya-L1 from Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
According to the Bengaluru-based national space agency, the spacecraft will be positioned in a halo orbit around the Sun-Earth system's first Lagrange point, L1. This location is roughly 1.5 million kilometres from Earth, where the Sun and Earth's combined gravitational pull permits a spacecraft to remain nearly stationary to the Sun.
It was noted that a satellite orbiting the L1 point had the primary benefit of continuously viewing solar activities without occultation/eclipses, reported the Economic Times.
Significance Of The Mission
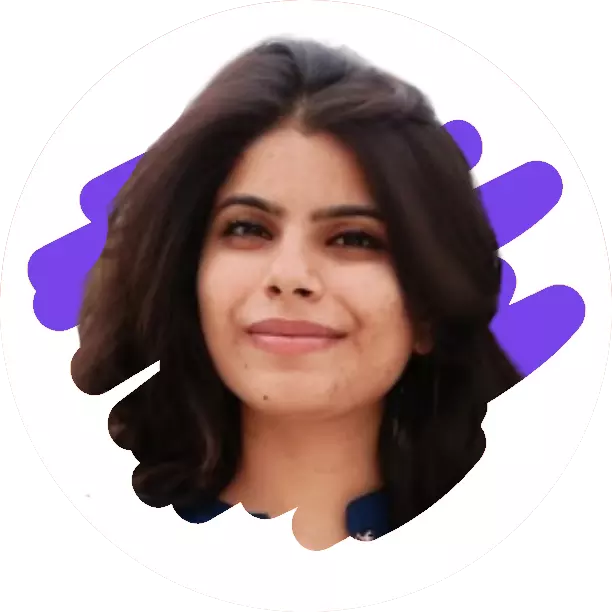
Aditya-L1 has seven payloads that use electromagnetic and particle detectors to study the photosphere, chromosphere, and the Sun's outermost layers (the corona). Three payloads conduct in-situ particle and field studies at the Lagrange point L1, while four payloads see the Sun directly from the unique vantage point of L1.
According to ISRO's website, some of the mission's scientific objectives are to study solar upper atmospheric (chromosphere and corona) dynamics and understand the physics of the solar corona and its heating mechanism.
The difference between the Sun's upper atmosphere's temperature of 1,000,000 K and its lower temperature of 6,000 K is one of the most significant unresolved problems in the study of solar physics. The mission will capture near-simultaneous photos of the many layers of the Sun's atmosphere, revealing how energy is routed and transported from one layer to the next.
Why Was Project Renamed?
The project was initially proposed as Aditya-1, a 400 kg class satellite carrying a single payload, the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC). It was then renamed 'Aditya-L1 mission' since the satellite was positioned in the hallowed orbit of the Sun-Earth system's Lagrangian point 1 (L1).
With the addition of multiple payloads, this project also gives solar scientists from around the country the option to engage in space-based instrumentation and observations. According to ISRO's website, the enhanced Aditya-L1 project would provide a thorough knowledge of the Sun's dynamic processes and answer some significant problems in solar physics.
Also Read: ISRO's 2nd Launchpad Brings TN's Kulasekarapattinam On Global Scientific Map, Know All About It
 All section
All section