Credist: Chalmers University of Technology, Pixabay
Rechargeable Cement-Based Batteries Could Make Future Buildings Sustainable: Study
Writer: Devyani Madaik
A media enthusiast, Devyani believes in learning on the job and there is nothing off limits when it comes to work. Writing is her passion and she is always ready for a debate as well.
India, 25 May 2021 2:32 PM GMT
Editor : Madhusree Goswami |
A mountain girl trying to make it big in the city. She loves to travel and explore and hence keen on doing on-ground stories. Giving the crux of the matter through her editing skills is her way to pay back the journalism its due credit.
Creatives : Devyani Madaik
A media enthusiast, Devyani believes in learning on the job and there is nothing off limits when it comes to work. Writing is her passion and she is always ready for a debate as well.
The batteries could also be coupled with solar cell panels, to provide electricity and become the energy source for monitoring systems in highways or bridges
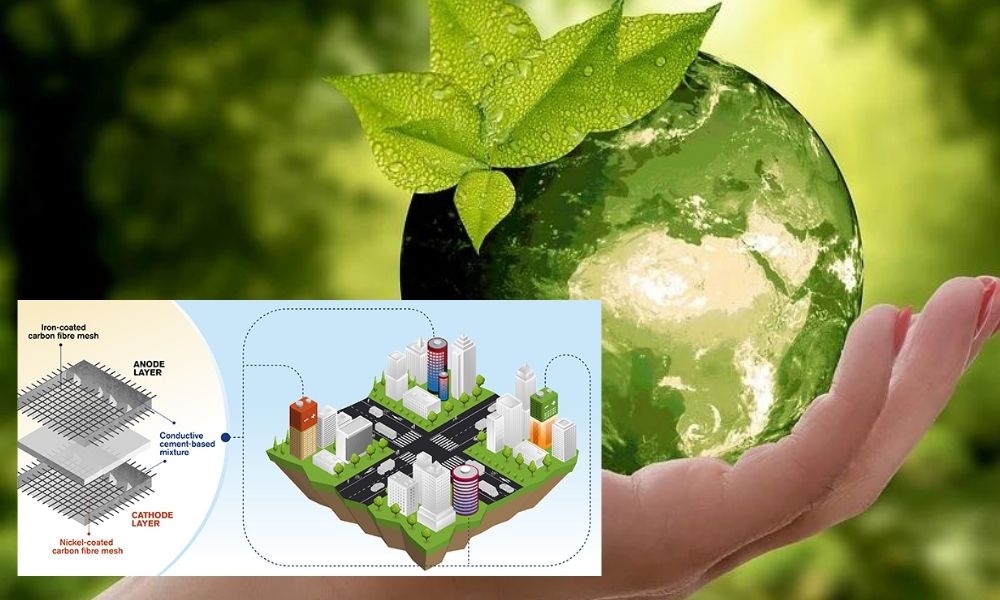
Sweden's Chalmers University of Technology has developed a unique concept for rechargeable batteries made out of cement. Developed by scientists associated with the Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, the concept includes multiple storey buildings storing energy like a giant battery.
The outlining concept caters to the need for sustainable building materials for the future. This is the world's first such concept for a rechargeable cement-based battery.
The material involves a cement-based mixture mixed with small amounts of short carbon fibres, which would increase the conductivity and flexural toughness, the report read. A metal-coated carbon fibre mesh, iron for the anode and nickel for the cathode will be embedded with the mixture.
"This particular idea that we have developed – which is also rechargeable – has never been explored before. Now we have proof of concept-at-lab scale," Mercom India quoted Emma Zhang, a former associate at the university.
According to the report, the battery is produced with an average energy density of 7 Wh per square meter (or 0.8 Wh per litre). The density is low in comparison to commercial batteries.
The most important aspect remains that it is rechargeable. "It could also be coupled with solar cell panels, for example, to provide electricity and become the energy source for monitoring systems in highways or bridges, where sensors operated by a concrete battery could detect cracking or corrosion," Zhang added.
Why Is The Idea Revolutionary?
The concept of using structures and buildings in this manner could be revolutionary as it would offer an alternative solution to the energy crisis by providing a large volume of energy storage.
 All section
All section