Picture Credit: FirstPost
Know About 'Indian Independence Act', Which Partitioned British India Into Two Dominions
Writer: Ronit Kumar Singh
A confident and reliable journalist who always desires to toss the unheard voices. I cover politics and governance extensively through stories.
India, 18 July 2022 8:12 AM GMT | Updated 18 July 2022 8:17 AM GMT
Editor : Snehadri Sarkar |
While he is a massive sports fanatic, his interest also lies in mainstream news and nitpicking trending and less talked about everyday issues.
Creatives : Ronit Kumar Singh
A confident and reliable journalist who always desires to toss the unheard voices. I cover politics and governance extensively through stories.
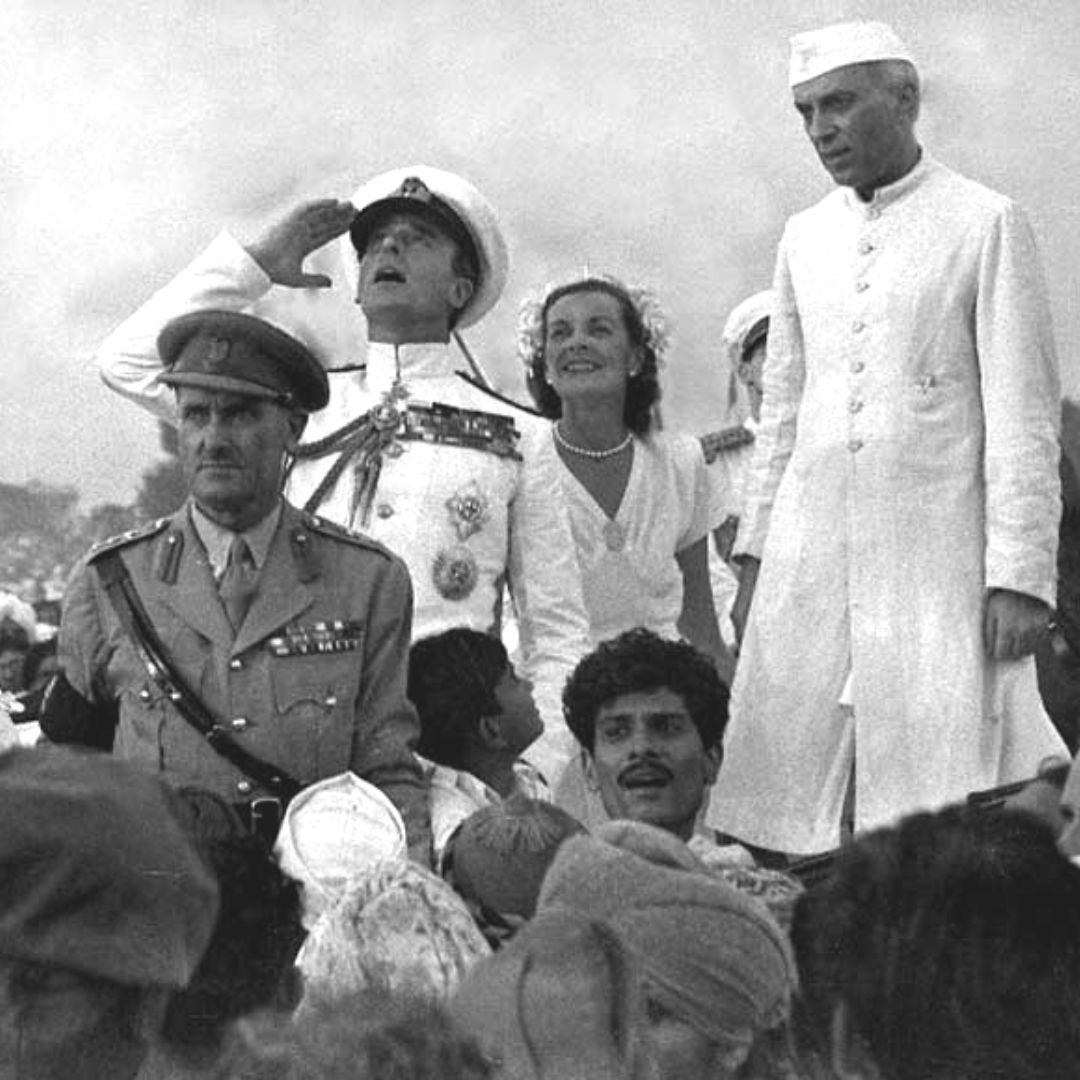
On July 18, 1947, the 'Indian Independence Act' came into force after it received Royal assent. The act partitioned British India into the two new independent dominions of India and Pakistan.
The Indian Independence Act of 1947 came into force on July 18 after it received royal assent. The British parliament passed this resolution which partitioned India into the newly independent dominions of India and Pakistan. Based on the Mountbatten Plan, also known as the June 3 Plan, the legislation was constituted by Clement Attlee's Labor administration.
As it was the final plan for the Independence of India, the representatives of the Muslim League, Sikh community, and Indian National Congress (INC) came to an agreement with the British administration and passed this resolution. After the Indian Independence Act of 1947, the Republic of India and Pakistan came into existence on August 15, 1947. Both the countries became independent dominions which means a self-government model of governance.
After the independence plan was passed in the parliament, the use of the term 'Emperor of India' by the British Monarch was also abolished.
Constitution Of New Dominions
British India, after conversion into two newly independent nations, India and Pakistan, engaged in the formation of new rules and laws- a constitution to run the country. Wikipedia report claims that until the time of making the new constitution, the provinces were to be governed by the Government of India Act, 1935.
Interestingly, the new constitution of India, which came into effect on January 26, 1950, consists of 395 articles under 22 parts (initially). But almost half of the articles of the constitution of India were taken from the Government of India Act, 1935, which was constituted during British rule.
Under the Indian Independence Act, 1947, the British administration established the office of the Governor-General in the two new dominions of India and Pakistan as the representative of the British crown. The governor-general was also empowered to divide the new nations' rights, duties, territories, and assets.
In addition, the governor-general held the power to amend and adopt the Government of India Act 1935 if necessary. However, the power remained valid till March 31, 1948, after which it was transferred to the constituent assemblies.
Also Read: Presidential Elections 2022: Polling Begins To Elect India's 15th President As MLAs & MPs Cast Votes
 All section
All section