Image Credits: Unsplash (Representative)
'Vaccinated Mothers Can Pass On Immunity To Babies Through Antibodies In Breast Milk': Study
Writer: Tashafi Nazir
For most people, journalism sounds hectic and chaotic. For her, it's a passion she has been chasing for years. With an extensive media background, Tashafi believes in putting efforts on presenting a simple incident in the most interesting way.
Others/World, 26 Aug 2021 7:58 AM GMT
Editor : Palak Agrawal |
Palak a journalism graduate believes in simplifying the complicated and writing about the extraordinary lives of ordinary people. She calls herself a " hodophile" or in layman words- a person who loves to travel.
Creatives : Tashafi Nazir
For most people, journalism sounds hectic and chaotic. For her, it's a passion she has been chasing for years. With an extensive media background, Tashafi believes in putting efforts on presenting a simple incident in the most interesting way.
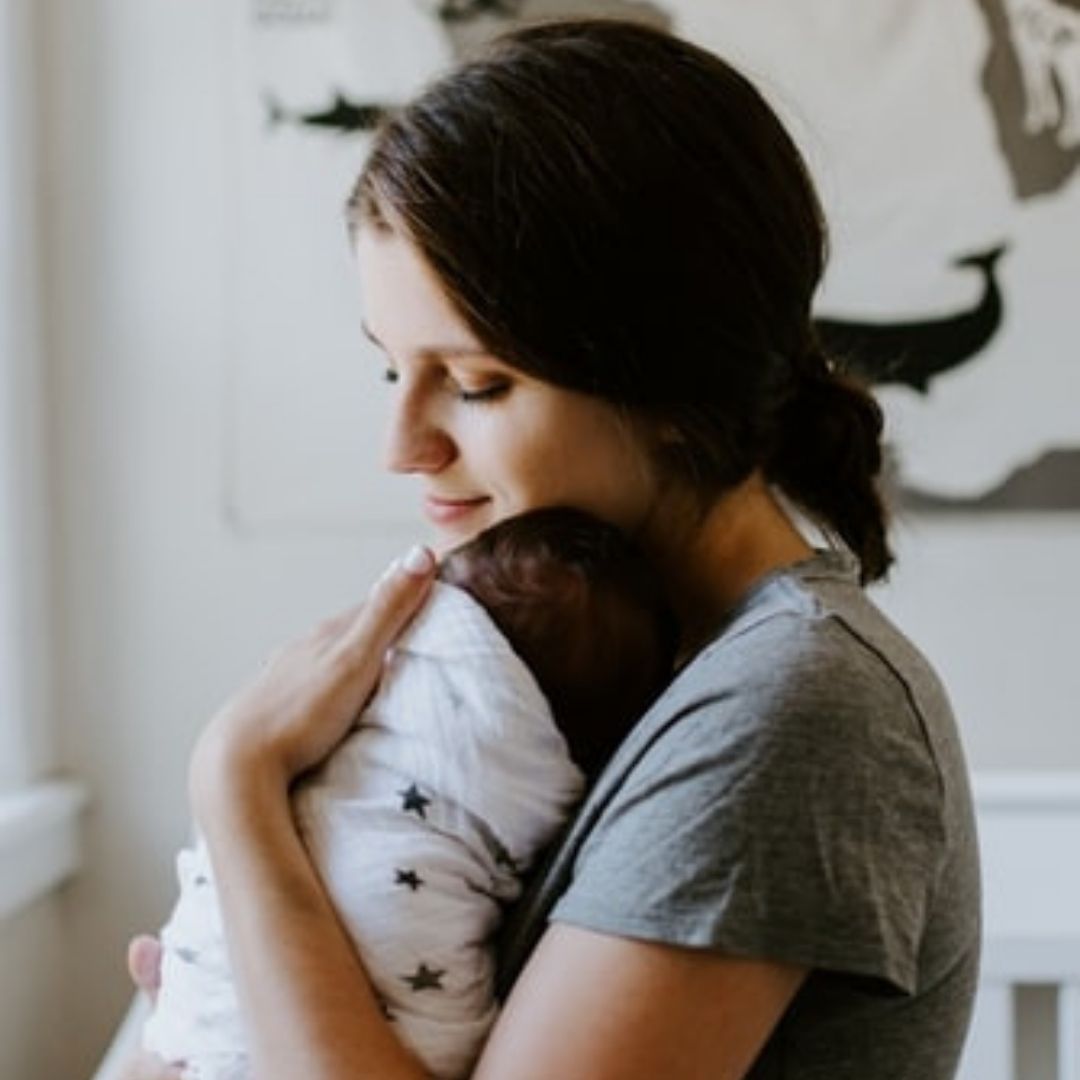
According to the research, published in the journal Breastfeeding Medicine, immunisation has been found important in protecting both mother and the baby, which becomes yet another compelling reason for pregnant ladies or nursing women to get jabbed.
The breast milk of lactating mothers who have received their shots of COVID-19 vaccine consists of an essential amount of antibodies that can help protect babies from the illness, according to a new study.
The research published in the journal Breastfeeding Medicine stated that immunisation can help protect both mother and the baby, which becomes another compelling reason for pregnant ladies or nursing women to get jabbed.
"The findings of the study reveal that immunisation notably helps to increase antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in breast milk. It suggests that vaccinated mothers can pass on this immunity to their babies," Joseph Larkin, a senior study author and an associate professor at the University of Florida, US said, reported NDTV.
When babies are born, their immune system is not fully developed and unable to fight the virus independently, the researchers noted. Besides, they are too young to show a response to different types of vaccines.
Nursing Mothers Provide Infants With Passive Immunity
"As this is a vulnerable period, breast milk allows nursing mothers to pass on the immunity to their babies," said Josef Neu, study's co-author and a professor at the University of Florida, according to NDTV.
The study was conducted between December last year and March 2021. Twenty-one nursing health care workers, who had never been infected with COVID-19 were recruited. The mother's breast milk and blood samples were taken before vaccination, after the first and second shot respectively.
Robust Antibody Response After Second Dose
Lauren Stafford, a doctoral student in Larkin's lab, explained that a strong antibody response was reported in the blood and breast milk after the second vaccine dose. This response was 'hundred-fold increase compared with levels before vaccination.'
"Typically, pregnant women are immunised against cough and other kinds of flu as these can result in illnesses for infants. Babies also have the possibility to contract COVID-19. Therefore, routine vaccination of mothers against COVID-19 could be something we look forward in the future," said Vivian Valcarce, from the University of Florida, as per NDTV.
The team is researching how breast milk containing COVID-19 antibodies gained through immunisation protects babies who consume it.
"We would like to know if infants who consume breast milk containing these antibodies develop their own immunity against the virus," Larkin added.
The researchers said many other studies conducted across the globe also show antibodies in the breastmilk of vaccinated mothers which reaffirms their study.
Also Read: Karnataka Plans To Provide Cost-Effective Cancer Medicines By Using CSR, Govt Funds
 All section
All section