Image Credit: The Times of India
COVID Could Derail India's Tuberculosis Elimination Programme: ICMR Journal
Writer: Madhusree Goswami
A mountain girl trying to make it big in the city. She loves to travel and explore and hence keen on doing on-ground stories. Giving the crux of the matter through her editing skills is her way to pay back the journalism its due credit.
India, 13 July 2021 9:58 AM GMT
Editor : Ankita Singh |
A literature lover who likes delving deeper into a wide range of societal issues and expresses her opinions about the same. Keeps looking for best-read recommendations while enjoying her coffee and tea.
Creatives : Madhusree Goswami
A mountain girl trying to make it big in the city. She loves to travel and explore and hence keen on doing on-ground stories. Giving the crux of the matter through her editing skills is her way to pay back the journalism its due credit.
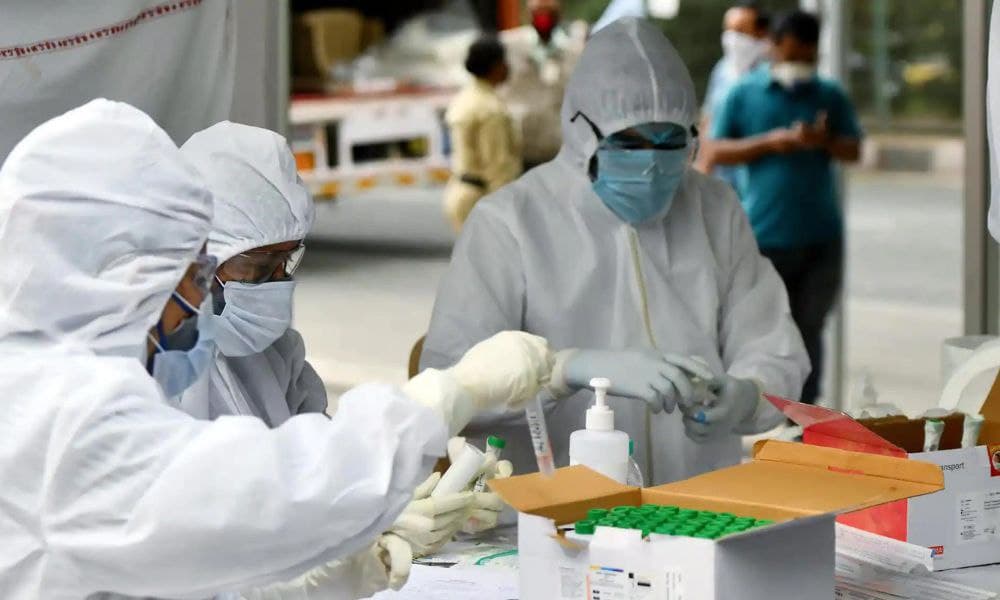
An ICMR journal noted that India may not be able to achieve its plan of eradicating TB by 2025 because of the focus and diversion of resources to COVID.
The pandemic could derail India's tuberculosis elimination programme as per an editorial in the Indian Journal of Medical Research (IJMR), a journal published by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has noted. The country recorded a 25 per cent fall in counts of new tuberculosis patients during the first half of 2021 compared with the corresponding period in 2019.
The elimination programme had registered 995,639 patients from the government and private sector between January 1 and July 12 this year, about 25 per cent of the 1.33 million notified in the same period in 2019, or the pre-COVID era. The editorial noted that India may not be able to achieve its plan of eradicating TB by 2025 because of the focus and diversion of resources to COVID, reported The Print.
Tuberculosis Cases Lower In Number
The number of new TB cases notified so far this year is slightly lower than the 1,000,580 cases notified between January 1 and July 12 in 2020. After sharp falls in registrations during the early months of the pandemic last year, the numbers had increased.
The TB elimination programme seeks to reduce India's incidence of the disease from 217 per 100,000 population in 2015 to below 77 per 100,000 by 2025 and reduce deaths from tuberculosis from 32 per 100,000 in 2015 to less than 3 per 100,000 by 2025. The fall in notifications has caused concerns among public health experts that many TB patients could remain undiagnosed and untreated.
Other Related Issues
The article pointed out that other issues such as over-utilisation of laboratories meant for TB work, re-deployment of care workers, difficulty in movement of TB patients and supervisors to supervise treatment and lack of contact-tracing will adversely affect the outcomes.
In December 2020, India detected around 1,74,000 new TB cases, close to around 1,79,000 patients registered in December 2019. But as COVID cases began to rise after mid-February this year, doctors say, diagnostic services for TB patients weakened again.
 All section
All section