All You Need To Know About Hepatitis - Causes, Symptoms And Treatments
null, 11 Jun 2016 7:00 AM GMT | Updated 9 July 2022 4:43 PM GMT
What is hepatitis?
Hepatitis, simply put, implies inflammation of the liver. Inflammation is the body's response to infection, cellular injury, or pathology caused by genetic disorders. Infectious hepatitis is caused by viruses named hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. Of these, hepatitis B is one of these infections. Although most cases are self-limiting and heal without any complications, those which do progress have a very severe outcome. How does it occur? The virus is present in an infected individual's blood. Spread occurs by injection of virus into the bloodstream.
The common incidents involved are transfusion with infected blood, needle prick injuries, infected needles in case of intravenous drug abusers. The virus specifically resides in the liver and destroys the liver cells.
What are the symptoms?
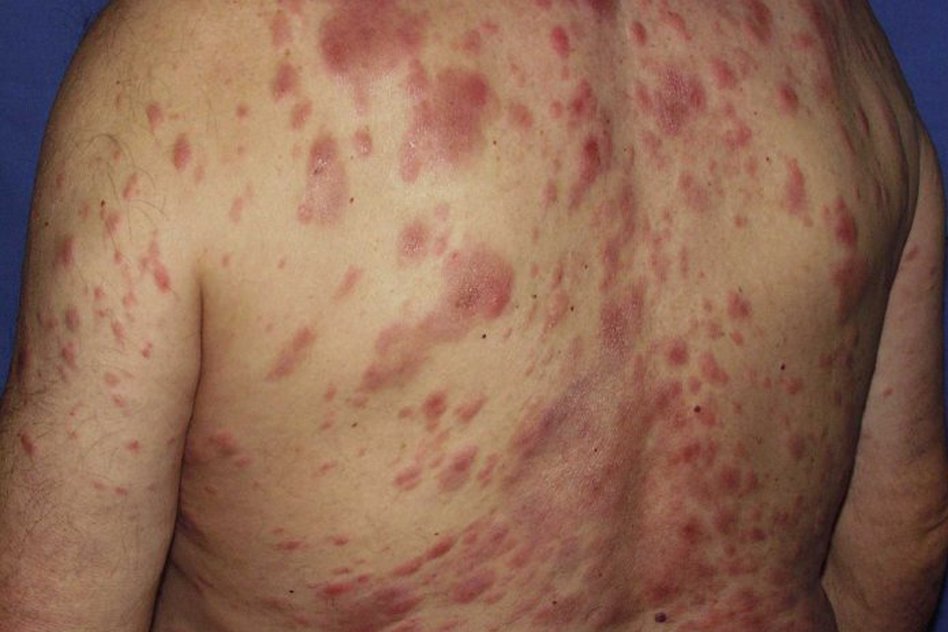
Asymptomatic incubation period -Prodromal features of generalised weakness, malaise, nausea, vomiting, and fever -Symptoms of hepatitis: jaundice, which may be seen as yellowing of the eyes, right upper abdominal pain, loss of appetite, fever, nausea and vomiting. Following the acute phase, most patients undergo remission, either spontaneously or after treatment.
Some cases, however, progress to the chronic state, which can precipitate several complications:
-Liver cirrhosis which occurs due to the destruction of normal liver cells, and formation of scar tissue in the liver. As the cells are destroyed, liver function fails, which can be seen in the form of swelling of the abdomen and feet, easy bruising, slowed clotting of blood, gonadal changes, and malabsorption.
-Portal hypertension which can lead to bleeding from varices in the esophagus, stomach or the rectum. Patients notice blood in stools or vomitus, black stools, or dark brown vomitus. As a precaution, blood noticed in the vomitus or stool must always be reported, as it often indicates an underlying disease.
-Hepatic encephalopathy: the liver clears the body toxins; with liver failure, these toxins enter the bloodstream, reach the brain and cause severe features like excessive daytime sleepiness, personality and behavioural changes, alteration of sensorium.
-Hepatocellular carcinoma, or liver cancer.
How can it be cured?
In the acute phase, supportive treatment is provided. In addition, interferons to enhance the body's immune response to kill the virus, and antiviral drugs like lamivudine or tenofovir may be given to ascertain cure. For late cases of cancer or severe cirrhosis, liver transplantation is the only treatment. These drugs must be prescribed only by a registered doctor, after appropriate examination and tests to diagnose the disease.
Can it be prevented?
Vaccines are now available, which are prescribed and injected by the doctor as three doses. The second dose is given a month after the first dose, the third dose is given five months after the second dose. In addition, the hepatitis B vaccine is now a part of the national immunisation scheme. Also, nowadays, blood donated for transfusion is almost always tested for diseases like hepatitis B, HIV-AIDS, to prevent transmission. Disposable needles are used for injections. As a precaution, make a habit of ensuring a fresh needle is used every time. Hepatitis B is an easily preventable disease, and if diagnosed early, it can be cured. We should all take preventive measures, and be on the lookout for any symptoms of the disease.
 All section
All section