Image Credits: Youtube
Digital Platform Developed To Map Non-Compliant Brick Manufacturing Units To Tackle Air Pollution
Writer: Palak Agrawal
Palak a journalism graduate believes in simplifying the complicated and writing about the extraordinary lives of ordinary people. She calls herself a " hodophile" or in layman words- a person who loves to travel.
India, 19 Dec 2020 1:15 PM GMT
Editor : Prateek Gautam |
A free soul who believes that journalism, apart from politics, should stand for social cause and the environment.
Creatives : Rajath
A free spirit who find meaning in life with the virtue of creativity and doing job par its excellence, animal lover and traveller by heart.
United Nations Development Programme’s Accelerator Labs, the arm working towards tackling sustainability challenges, in partnership with Nottingham University has developed 'Geo AI Platform' to map such brick manufacturing units which flout the mandatory environmental regulations and are responsible for higher emissions of harmful gases.
Air pollution, one of the most severe forms of contamination of the environment, has led to India accommodating as many as 21 out of 30 most polluted cities in the world.
According to the World Air Quality Report 2019 compiled by IQAir Air Visual, six cities from India are in the top ten list of most polluted cities hinting at the grave situation plaguing the country.
A substantial portion of the pollution is caused by industrial pollution followed by vehicles, crop burning and fireworks. Air pollution reportedly contributes to the premature deaths of 2 million Indians every year.
Constant deterioration in the quality of air is making headlines, with the state and the union government wrestling to get a grip on the sources. Stubble burning, rise in the emission of hazardous gases owing to industrial pollution, the incessant use of dirty fossil fuels by industries, unrestrained construction activities, heaps of uncovered dust around the construction sites are key contributors of air pollution.
Air Quality Index is a numerical scale used to measure and report air quality of an area on a given day. Eight pollutants — PM10, PM2.5, NO2, SO2, CO, O3, NH3, and Pb are the major parameters taken into consideration while deriving AQI of a region. It reveals how air pollution affects one's health within a short time period.
Finding The Concern & Fixing With Solutions
To understand the rising air menace, United Nations Development Programme's Accelerator Labs, the arm working towards tackling sustainability challenges reviewed the situation and stated that brick manufacturing industries are one of the contributing sectors to industrial emissions.
UNDP Accelerator Lab is part of the world's largest and fastest learning network focussing on the challenges posed by developmental activities. 60 labs serve 78 countries to find radical solutions to the significant development challenges. Such labs around the world are testing not just new solutions but new ways of working to address social and environmental challenges which focus on running quick experiments to help understand components of interventional solutions. Solutions mapping, exploration and experimentation are some of the tools used by the labs.
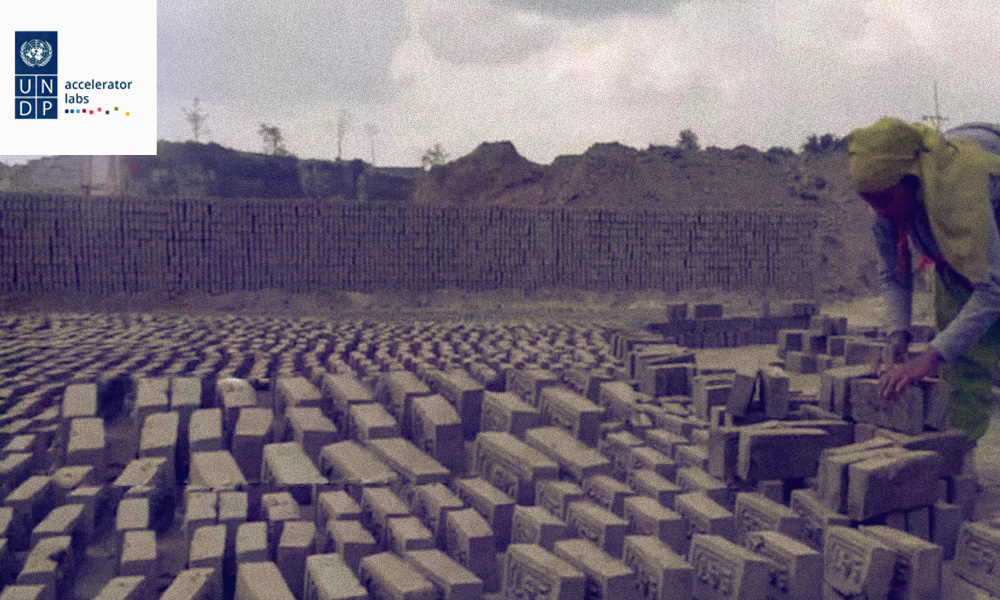
The brick kiln industry is a booming industry as the demand for bricks is increasing due to fast economic growth and urbanization. The raw materials used for brick production are soil clay or sediments from rivers, which are rich in fine particles. Burning of coal during the process produces a high level of sulphur dioxide and black carbon.
In India, fire clay bricks are produced in about 42000 small and medium scale brick kilns which operate normally using 4–5 million metric tonnes of coal each year.
UNDP Accelerator Labs which has been taking up several initiatives to combat air pollution conducted a study in partnership with. The research titled 'Fighting Slavery From Space' would help fight the
The research revealed that besides being a major contributor to air pollution, these brick kilns were also hotspots for bonded child labour. It, therefore, took steps to come up with solutions to inform various stakeholders about the hotspots that are at the intersection of both development challenges.
The research team has come up with a digital technology platform developed to monitor the hotspots and provide precise geospatial coordinates of all brick kilns. Reports have suggested that every year more than 140 million Indians are exposed to severe air pollution when the AQI crosses the hazardous mark of 300 during winters.
The Geo AI platform, making use of the gathered data and artificial intelligence tools, has been developed to help environmental regulators take actions on non-compliant brick manufacturing units. The brick manufacturing units have distinct spatial features that can be detected from satellite imagery using object detection algorithms.
It further revealed that as many as 37,000 units engaged in the process of making bricks were identified and filtered down to list the ones operating under unfavourable conditions. The results showed that such non-compliant units were flagged in the states of Haryana and Bihar.
The digital platform uses a variety of criteria to filter the non-compliant units. Minimum distance from a water body, the minimum distance between adjacent brick kiln, distance from schools and hospitals are some of the factors, specified by environmental regulators, which are taken into consideration by Geo AI platform.
Availability of such crucial information could assist the regulators in taking appropriate action regarding such units responsible for flouting environmental norms and emitting harmful gases.
Also Read: Indian Entrepreneur Among UN Environment Agency's 'Young Champions Of The Earth' Winners
 All section
All section