Kisan Diwas: How Chaudhary Charan Singh Helped Empower Weaker Sections In India
Writer: Shweta Singh
She is a Journalism graduate from Delhi University, She has previously worked as a voice over artist for various cuisines and clothing brands. She is specialised in content writing, hosting anchoring and voice over.
India, 23 Dec 2021 8:29 AM GMT | Updated 23 Dec 2021 8:42 AM GMT
Editor : Snehadri Sarkar |
While he is a massive sports fanatic, his interest also lies in mainstream news and nitpicking trending and less talked about everyday issues.
Creatives : Snehadri Sarkar
While he is a massive sports fanatic, his interest also lies in mainstream news and nitpicking trending and less talked about everyday issues.
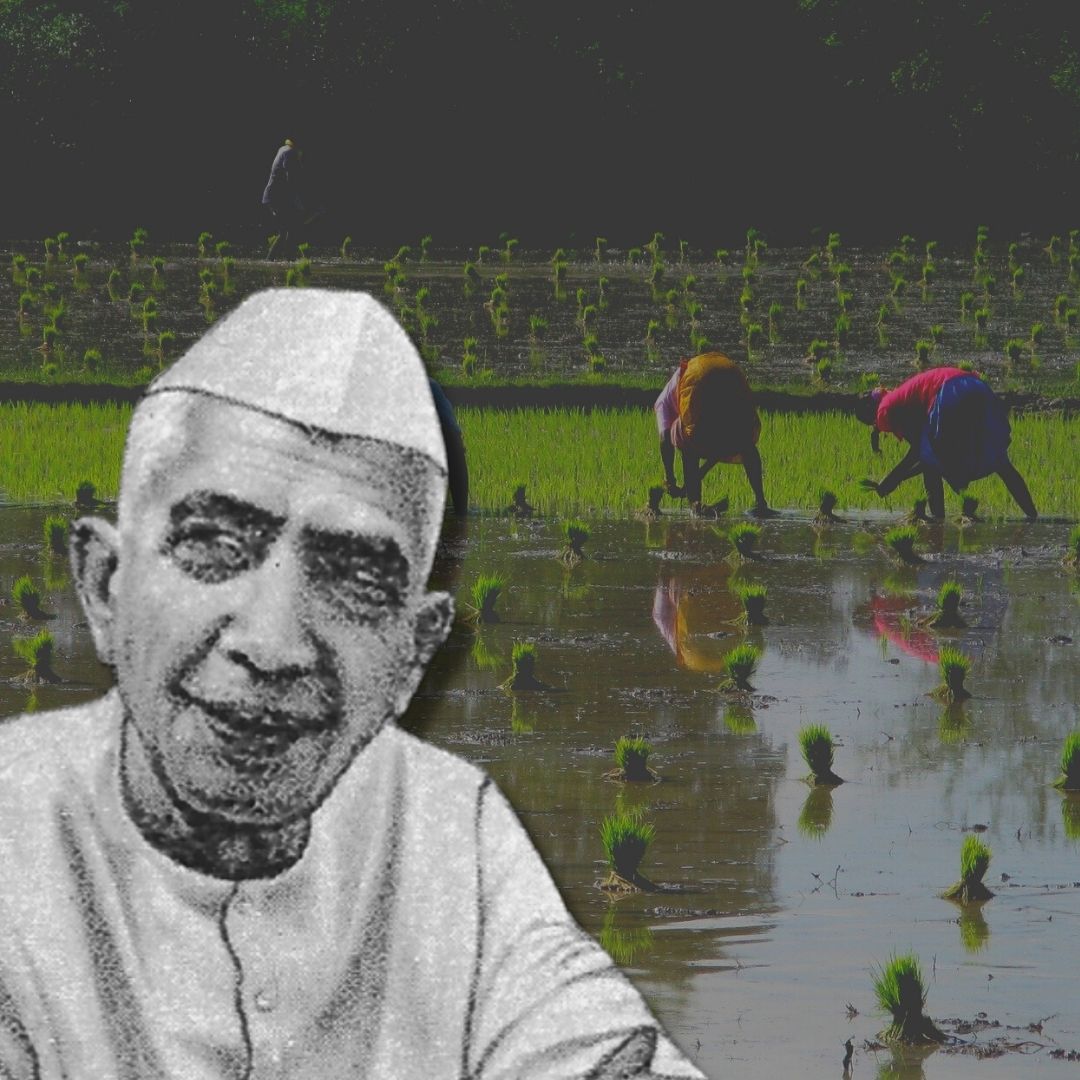
Every year, December 23 is celebrated to acknowledge the contribution made by the farmers in our daily lives. The day also marks the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, the fifth Prime Minister of India and served twice as Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh.
India observes National Farmers Day or Kisan Diwas every year on December 23. The day is commemorated to acknowledge the contribution made by farmers in our lives.
The day also marks the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, the fifth Prime Minister of India and served twice as Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh. Chaudhary Charan Singh was born to a rural peasant jat family in Uttar Pradesh on December 23 1902. Singh played a vital role in re-organizing the country's political economy and was the chief architect of land reforms in UP.
In 1939, he introduced Debt Bill to relieve the peasantry from moneylenders and abolished Zamindari from UP by bringing in Zamindari Abolition Act 1950. In 1960 Singh brought in Land Holding Act 1960, setting a limit of land held by an individual or corporation, also known as the land ceiling, thereby allowing the government to reapportion surplus land to landless.
Best Agricultural Schemes Introduced by Central Government
The government of India has introduced various Schemes to safeguard the interest and rights of the farmers.
PM-Kisan Yojana
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Yojana, introduced in 2018, aims at providing Rs. Six thousand in three instalments per year as minimum income to 120 million small and marginal farmers of India with less than two hectares of landholding.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Mandhan Yojana
The Scheme aims to provide a minimum pension of Rs. 3000/month to marginalized farmers on attaining the age of 60. The farmers are required to make monthly of Rs 55 to 200 depending on their age as those between 18-45 can apply for the Scheme.
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana
The Scheme is an actuarial premium based Scheme where a farmer has to pay a maximum premium of 2 per cent for Kharif, 1.5 per cent for Rabi food & oilseed crops and 5 per cent for annual commercial or horticultural crops and the remaining part of the actuarial or bided premium is equally shared by the Central & State Government. An essential purpose of the Scheme is to facilitate quick claims settlement. The claims should be settled within two months of harvest subject to the timely provision of both yield data & share of premium subsidy by the State Government.
Kisan Credit Card Scheme
Introduced in 1998, The Scheme provides short term credit to cultivators in the agriculture, fisheries & animal husbandry sector to purchase equipment & for their other expenses as well. There are many banks that offer KCC, including SBI, HDFC, ICICI, Axis.
Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana
The Scheme aims to promote organic cultivation in India to improve soil health and organic content in India, thereby boosting the net income of the farmers. It targeted to cover an area of 5 lakh acre through 10,000 clusters of 50 acres each, in 2015-16 to 2017-18.
National Agriculture Market (e-NAM)
National Agriculture Market gives an e-marketing platform at the national level and supports the creation of infrastructure to enable e-marketing. This new market process is revolutionizing agriculture markets by guaranteeing better price discovery. It also brings in transparency & competition to enable cultivators to get improved remuneration for their produce moving towards 'One Nation One Market', as per Krishi Jagran.
Also Read: Covishield Jab Protection Against COVID-19 Wanes Just After 3 Months: Lancet Study
 All section
All section