Image Credit- Pixabay, Twitter/Masood Manna
Hijab Controversy: A Result Of Mixing Education And Politics On Grounds Of Religion?
Karnataka, 4 Feb 2022 1:15 PM GMT | Updated 4 Feb 2022 1:17 PM GMT
Editor : Snehadri Sarkar |
While he is a massive sports fanatic, his interest also lies in mainstream news and nitpicking trending and less talked about everyday issues.
Creatives : Shiva Chaudhary
A post-graduate in Journalism and Mass Communication with relevant skills, specialising in content editing & writing. I believe in the precise dissemination of information based on facts to the public.
The issue has been politicised in the religiously polarised climate, with ministers intervening between the students and educational authorities. For the last few years, visible religious symbols have emerged as a political issue in India.
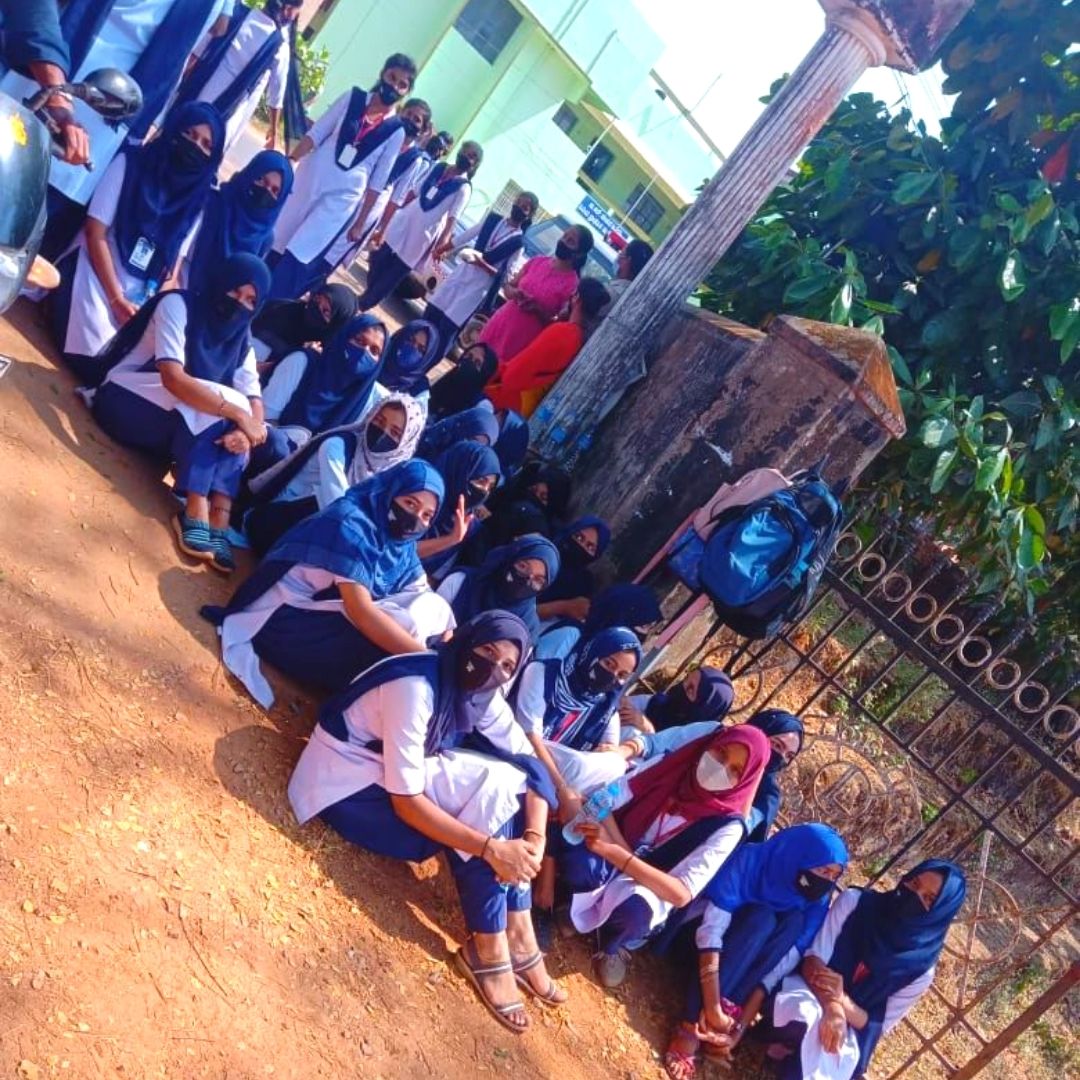
The controversy over wearing a hijab in an educational institution doesn't seem to perish soon. Yet again, the Muslim girls' students wearing hijabs were denied entry by authorities into a government pre-university college on Friday at Kundapur in Karnataka's Udupi district. It is the third day since the issue surfaced in the institution.
The students pushed into the college premises despite the authorities' strict orders that wearing hijabs would not be allowed as per the status quo on the dress code issued by the state government.
ANI quoted State Education Minister BC Nagesh saying, "They were not wearing the hijab earlier & this problem started only 20 days ago."
The entire issue started in early January when six students attended classes wearing hijab in violation of the dress code in classrooms at the government girls' pre-university (PU) college at Udupi.
Boys Wearing Saffron Scarves
The issue has been politicised in the religiously polarised climate, with ministers intervening between the students and educational authorities. As a mark of protest against allowing Muslim students to wear hijab inside the educational institution, boys have started to wear saffron scarves and raise religious slogans. However, in some institutes, boys were ordered to remove the scarves and follow the dress code.
But here, the question arises of the limitation to following religious symbols. Is it only about practising religion, or is it a result of mixing education and politics on the grounds of religion?
Why All Controversy Over Hijab?
On February 3, Shashi Tharoor, a politician associated with the Indian National Congress, supported the protesting Muslim girls and asked some blunt questions about religious attire.
He said, "It's been a strength of India that everyone is free to wear what they want. If the hijab is disallowed, what about the Sikh turban? The Hindu's forehead mark? The Christian's crucifix? This college is going down a slippery slope. Let the girls in. Let them study. Let THEM decide."
Visible Religious Symbol
Controversy over religious symbols such as Muslim skullcap/hijab, Christian crucifix, etc., are not a new thing globally. India is a diverse country with several religions being practised by its citizens. But for the last few years, visible religious symbols has emerged as a political issue in the nation.
The Indian constitution provides 'Freedom of Religion' as a fundamental right guaranteed by articles 25 to 28. Every citizen of India has a right to practice and promote their religion peacefully.
However, as a bitter truth, numerous incidents of religious intolerance have resulted in riots and violence, such as Anti-Sikh Massacre in 1984, the Anti-Hindu Riots in 1990, Gujarat Riots in 2002, Anti-Christian Riots in 2008 and very recent Delhi Rioys in 2020.
Also Read: In Delhi, Women Account For 8% Women Drivers But Only 1% Accidents: Report
 All section
All section