Image Credit: LiveMint
Prevalence Of Delta Variant Among Specimens Sequenced Over Recent Weeks Surpassed 75%: WHO
Writer: Chahat Suri
Chahat is a diligent, lively and a competitive student who is on her way to explore the world. An individual with a creative outlook, offering unconventional ideas, who wants to broaden her horizons in broadcast media and content writing.
India, 23 July 2021 2:03 PM GMT
Editor : Madhusree Goswami |
A mountain girl trying to make it big in the city. She loves to travel and explore and hence keen on doing on-ground stories. Giving the crux of the matter through her editing skills is her way to pay back the journalism its due credit.
Creatives : Chahat Suri
Chahat is a diligent, lively and a competitive student who is on her way to explore the world. An individual with a creative outlook, offering unconventional ideas, who wants to broaden her horizons in broadcast media and content writing.
The WHO stated that despite making efforts to extend vaccination coverage, many countries across all six WHO regions continue to experience an escalation in the number of cases.
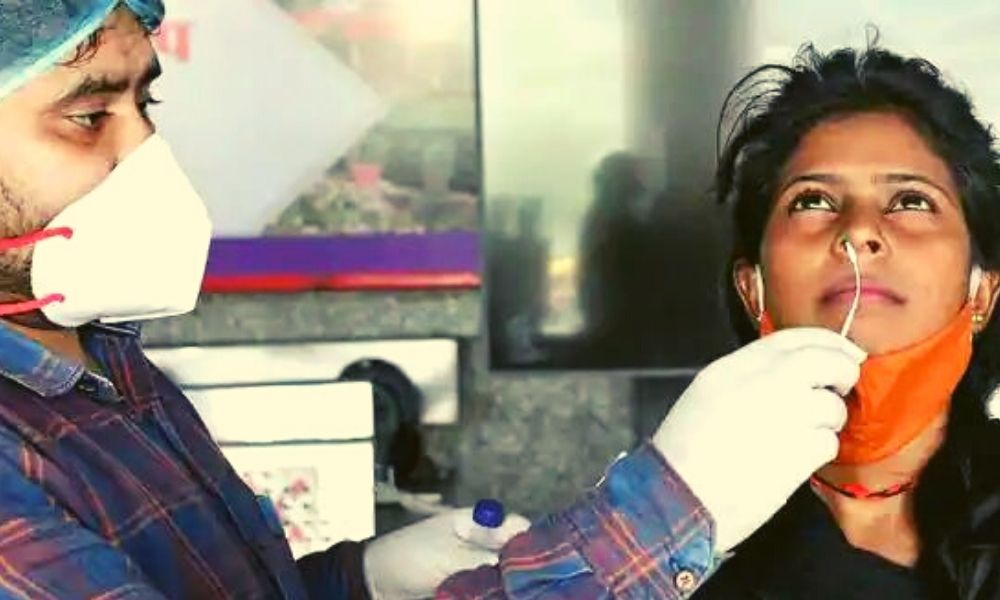
The prevalence of the highly-transmissible Delta variant of COVID-19 which originally surfaced in India, among the specimens sequenced over the past four weeks, exceeded 75 per cent in many countries worldwide, including India, China, Indonesia, Russia, Israel and the UK, the World Health Organization (WHO) has said.
In the COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update published on July 20, the WHO stated that despite making efforts to extend vaccination coverage, many countries across all six WHO regions continue to experience an escalation in the number of cases.
Global Count
Over the past week, the highest number of cases were reported from countries like Indonesia (350,273 new cases; a 44 per cent increase), the UK (296,447 new cases; 41 per cent increase), Brazil (287,610 new cases; 14 per cent decrease), India (268,843 new cases; 8 per cent decrease) and the US (216,433 new cases; 68 per cent increase).
As of July 20, a total of over 2.4 million SARS-CoV-2 sequences have been submitted to GISAID, the global science initiative and primary source that provides open access to genomic data. Around 9 per cent of the sequences submitted to GISAID, have been confirmed as the delta variant.
"According to GISAID data, as of 20 July, the prevalence of Delta variant among the other specimens sequenced over the past 4 weeks which exceeded 75 per cent in many countries worldwide including Australia, Bangladesh, Botswana, China, Denmark, India, Indonesia, Israel, Portugal, Russian Federation, Singapore, South Africa and the United Kingdom," the update said.
Rapid Replication
The update further said that due to the growing proof it is becoming increasingly evident that the transmissibility of the Delta variant is higher as compared to the non-Variants of Concern (VOCs) but the exact mechanism for the increase in transmissibility remains indefinite.
A recent study by China during the outbreak of the Delta variant cited that the time interval from the exposure of a quarantined population to the first positive Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) result is shorter for the Delta variant when compared to non-VOCs.
Moreover, the viral load of the first positive test of Delta infection was 1,200 times more higher than non-VOCs, suggesting that this variant of concern might replicate faster and can be more contagious during the early stages of infection.
Among the COVID-19 cases, the risk of hospitalisation, ICU admission and deaths due the Delta variant in comparison to non-VOCs increased by 120 per cent, 287 per cent and 137 per cent, respectively.
Other Variants
Globally, cases of the Alpha variant have been reported in 180 countries or territories, whereas 130 countries reported cases of the Beta variant; 78 countries cases of the Gamma variant and 124 countries reported cases of the Delta variant.
The deadly Delta variant was largely responsible for the massive second wave of COVID cases in the country.
Also Read : First Death Due To Bird Flu At AIIMS Delhi; Staff Under Isolation
 All section
All section